Glycoproteins of the envelope B. Tobacco mosaic virus arenaviruses and bunyaviruses are some examples of viruses with a helical capsid.
B The viral genomes can always act as mRNA.
. C The adenovirus uncoating begins during the release of the viral capsid from the endosomes 1 and is completed at the NPC 2 where there is a complex formed by the capsid Nup 358 Nup214 microtubules and kinesin. E is called a capsid protects the nucleic acid AND is involved in the recognition of host cell receptors by non-enveloped viruses. The dormant stage of a viruss existence characterized by Viral DNA injected into the host cell Viral DNA inserts itself into the hosts DNA where it remains inactive for days months or years.
______ infections are those which cells are infected yet show no cytopathic effects. C The virions of RNA viruses always contain an RNA-dependent RNA or DNA polymerase protein. CEpitopes or antigenic determinants.
The _____is an organelle which merges with a vacuole to allow digestion of engulfed structures from phagocytosis. A capsid is a protein shell that encloses the viral genome RNA DNA etc. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat.
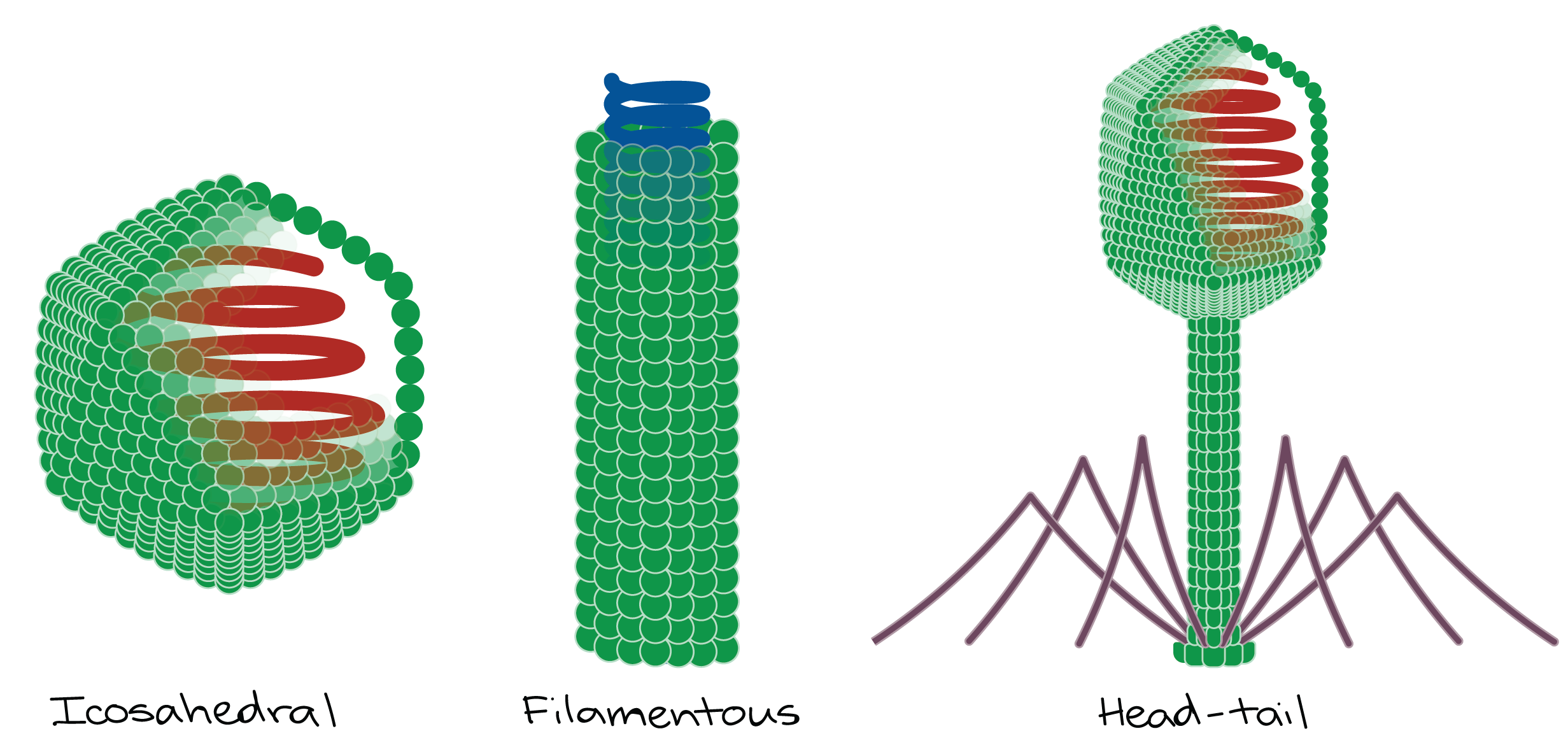
There are three main capsid shapes as described in the following. Virally infected cells can release interferon which promotes inflammation. O Interferon binds to normal uninfected cells stimulating the.
And are reliant on a host cell for their own reproduction. Identify which of the following are functions of the viral capsid or envelope. Which of the following best describes the function of cilia and flagella.
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus enclosing its genetic material. Which two of the following statements BEST describes all types of viruses that have an RNA genome. The viral offspring that rupture the cell and escape.
Once the capsid docks at the NPC the viral DNA is injected to the nucleus 2. Viral genomes vary greatly in size and may include from four genes to several hundred genes. A fatty membrane surrounding the virus.
Which öf the following statements best describes how that occurs. The main function of capsid are to protect and package the genetic material and any additional enzymes that are required to form a infectious virus into the virion. As the cell reproduces more cells are produced that have the viral DNA in them.
RNA versus DNA genome C. A capsid is a protein coat that protects the genetic material of the virus. Size and shape of the.
D They are always single stranded. The genetic material at the core. Possess a capsid composed of protein.
B Changes in viral proteins and their genes by mutation. This virus attacks the white blood cells immune cells of the human body. C The viral genome is recognized by the capsid that surrounds the host cell genome.
The mechanical stress caused by the binding to. A They always contain a gene encoding an RNA-dependent RNA or DNA polymerase. A capsid defines the shape of the virus.
Capsids come in about three different shapes although there can easily be more complex ones. D The spread of viral infection on a global scale like that which happened in 1918. Adherence to host cells.
A protein coat around the genetic material. Interferon will attract antibodies to the virally infected cell. Which of the following best describes viruses.
It consists of several oligomeric structural subunits made of protein called protomers. Double versus single strand genomes D. Size and shape of the capsid E.
Eventually the immune system cannot handle the viral invasion. Question 18 01 pts Which of the following best describes the action of interferon. In the attached file we have shown that viral capsids contain the viral genome packaged in a protein coat called the capsid.
BThe low molecular weight protein produced by animal cells in response to viral infections is. What name is given to a viral capsid that is shaped like a hollow tube with protein of walls. Capsid proteins are assembled in a circular manner resembling a stack of discs that are attached helically creating a central cavity as a place for the nucleic acid.
A The slow spread of viral infection in crowded environments. B Surface proteins on the virus are recognized by receptor proteins found in the plasma membrane of the host cell. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits which may or may not correspond to individual proteins are called capsomeres.
The size and shape of the prisoner proteins. The diameter of the capsid of a helical virus like TMV is determined by. Size of the viral capsomeres D.
A The viral genome matches the host cell genome. Which of the following best describes viral tropism. Which statement best describes a capsid.
A capsid is the outside coat of the virus. The viral capsid is. At minimum all viruses are composed of.
Interferon can penetrate the viral capsid and destroy the virus. The structure directly surrounding the viral nucleic acid is the ______ a coat of proteins. This makes the body prone to attack from other viruses and bacteria.
Viral nucleic acid enters the host cell and uses host cells replication and synthesis machinery in order to produce new nucleic acid molecules proteins for the capsid spikes and viral enzymes. C The production of new hybrid viral particles following the infection of a single cell by two viral types. A capsid is either helical icosahedral or complex.
Which of the following viral features is most apt to correlate with the size of the genome. Which best describes the lysogenic cycles.
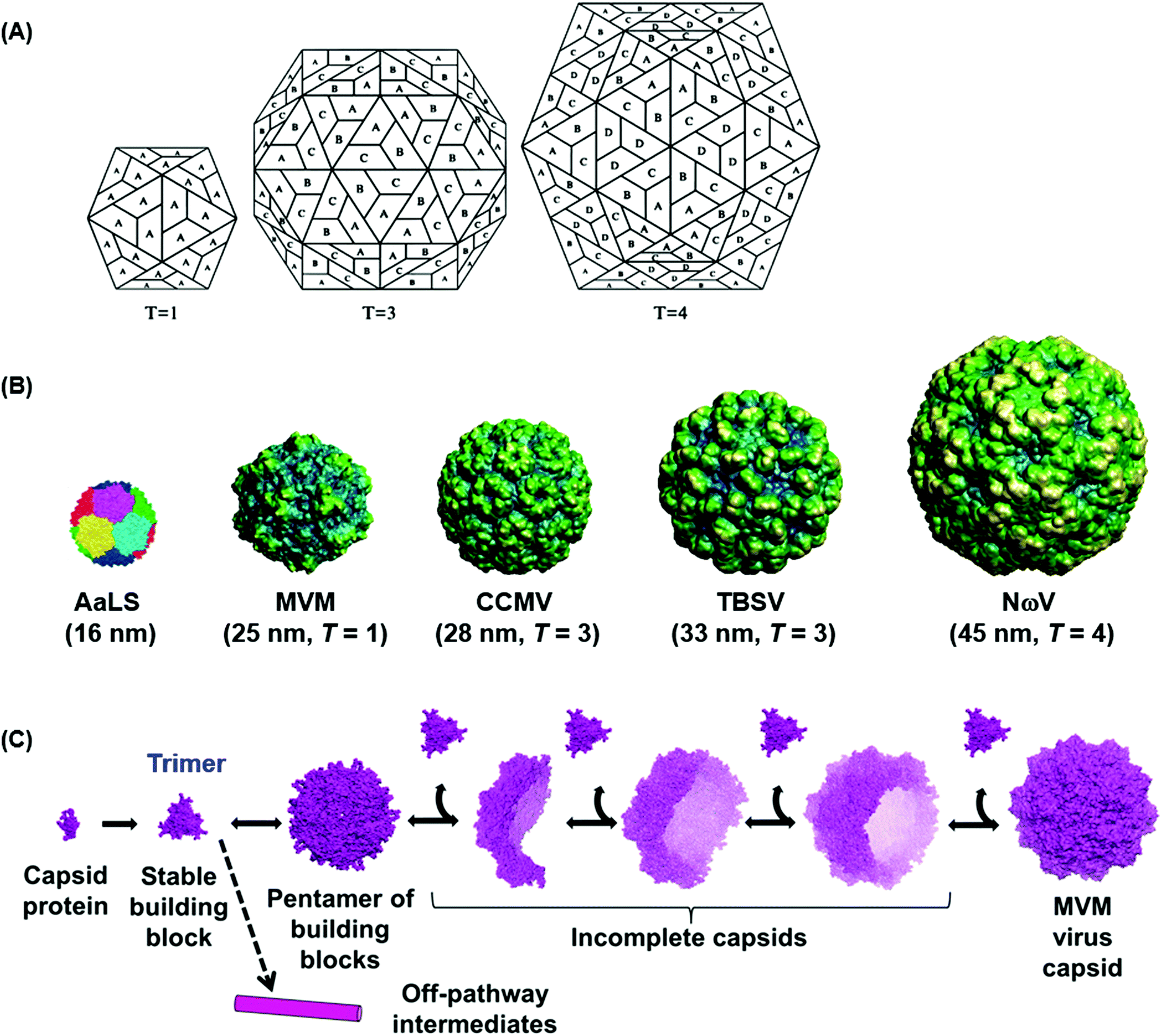
Synthetic Approaches To Construct Viral Capsid Like Spherical Nanomaterials Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C8cc03844a

Viral Capsid Assembly In The Nucleus And Transport To The Cytosol Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments